Contents
Trying to transfer bitcoin to the Ethereum blockchain directly is like getting an Android app to run on iOS — you won’t succeed unless you install an emulator. Different blockchains are like different worlds, and you need a common bridge to communicate between them.
A wrapped token is such an astronaut launched into the realm of another blockchain that will need a certain anchor to the value of the native cryptocurrency. It is a wrapped token because the original asset is placed in a “wrapper,” a digital vault. Being a wrapper, this token, like a virtual avatar, can be represented on someone else’s blockchain.
What is the point of this? Different blockchains offer different functionality. Sometimes it is advantageous to present bitcoin on an Ethereum or Tron blockchain for some specific transactions. Wrapped cryptocurrencies allow crypto-assets to be used in blockchains for which they are not native.
Still not clear? Don’t be frightened; below, we’ll explain how it works.
The brand new newsletter with insights, market analysis and daily opportunities.
Let’s grow together!
What is a wrapped token?
A wrapped token is a tokenized version of another cryptocurrency. It is pegged to the value of an asset, which can usually be exchanged back at any time. It is typically an asset not on the blockchain on which it is issued.
You might think that a wrapped token is similar to a stablecoin because it gets its value from another asset. In the case of a stablecoin, it is usually fiat currency. In the case of a wrapped token, it is an asset initially living in another blockchain.
Wrapped cryptocurrencies increase the usefulness and liquidity of smart contract platforms and popular decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. Other reasons for cryptocurrency portability may include exchanging ERC-20 tokens or using blockchain features that a crypto asset may not have in its chain.
For example, a wrapped bitcoin token can be instantly sent over a superfast blockchain, bypassing the limitations and slowness of the original bitcoin blockchain.
What types of wrapped tokens exist?
Since you cannot use tokens based on one blockchain in applications built on other blockchains, you will need wrapped tokens.
For example, Ethereum only supports ERC tokens. Therefore you still cannot use bitcoin or other blockchain tokens in DeFi applications built on Ethereum and vice versa. You will have to exchange these tokens for wrapped tokens compatible with Ethereum.
Most often, wrapped tokens live on Ethereum or in Binance Smart Chain. In the case of Ethereum, such tokens can be used to replace non-native Ethereum assets — tokens that are used on other platforms. Similarly, on Binance Smart Chain, various cryptocurrencies can be wrapped using Binance Bridge into BEP20 tokens. These can be bought, sold, or used for multiple purposes, such as farming (lending your funds at interest in cryptocurrency).
Interestingly, ETH is needed to pay for transactions in the Ethereum blockchain that came before the ERC-20 standard. Therefore it is not compatible with ERC-20 and cannot be a way to exchange directly with other ERC-20 tokens.
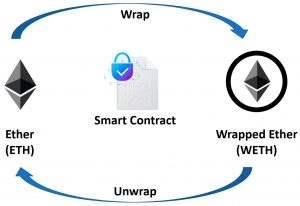
Thus to “wrap,” Ethereum needs to be converted into an ERC-20 token. To do this, you need to convert ETH to wETH. It creates a tokenized version of Ethereum. Wrapping ETH does not affect its value; the ratio remains 1:1. Wrapped Ethereum can be created by sending it to a smart contract that takes Ethereum and gives ERC-20 tokens in return.
You can read more examples of popular wrappers below.
How do wrapped tokens work?
Wrapped tokens are created and destroyed in a mutually reversible cycle consisting of an initial and an end-stage: “minting” and “burning.”
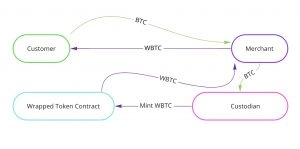
To understand how wrapped tokens work, let’s examine how they are constructed. To create a wrapped token, a custodian is required. A custodian is a trusted person who owns a certain amount of crypto assets. The value of the wrapped tokens created must be equivalent to the value of those assets 1:1.
The custodian is usually a:
- Merchant.
- A Multisig wallet (a type of wallet that requires multiple simultaneous signatures to access).
- DAO (decentralized autonomous organization).
- Smart contract.
A custodian receives a certain amount of cryptocurrency from someone who wants to trade on an Ethereum-based platform. The transferred BTC are then placed in a digital vault, frozen. At the same time, an equal amount of 1 WBTC is issued in the Ethereum blockchain.
The value of WBTC is linked to the value of BTC and changes in real-time due to the smart contract algorithm. If the client wants to exchange WBTC back to BTC, the client sends a request to the custodian. The custodian burns the WBTC and releases the BTC back from the vault. Proofs of transactions are stored on the blockchain. It is important to note that there is a fee (gas) for packaging and unwrapping the cryptocurrency.
What are the benefits of using wrapped tokens?
The most apparent advantage of wrapped tokens is that they help overcome the incompatibility problem. You can use tokens in the blockchain even if they are not originally native to it.
Second, wrapped tokens help build connections and help increase liquidity. Your capital is used more efficiently as you put idle assets to work.
Finally, wrapped tokens help you avoid additional fees and increase the speed of transactions. By choosing the proper blockchain, you have more flexibility to bypass all sorts of restrictions/challenges from the asset’s native blockchain.
What are the limitations of wrapped tokens?
Like everything else in the world, wrapped tokens are not without drawbacks. Such tokens do not allow true migration from blockchain to blockchain. That’s why there needs to be a third party present to create the wrapper. It means additional costs and dependencies.
Wrapped bitcoin tokens are no longer the coins you give away initially. When you create a wrapped token, you get a different virtual coin. This way, you can lose some of the original features of a particular asset.
Some platforms do not accept wrapped tokens for staking or farming, as do some exchanges and wallets.
While wrapped tokens are not ideal, they help connect different blockchains and markets. It removes barriers in the DeFi sector and helps cryptocurrencies work much more efficiently.
What are some examples of wrapped tokens?
As examples, let’s look at the most popular varieties of wrapped tokens.
- Wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC). As mentioned, wrapped tokens are digital tokens on a blockchain pegged to another blockchain’s cryptocurrency. So if you take bitcoin, for example, you would need to exchange your bitcoins for wrapped bitcoins (wBTC), which are Ethereum-based digital tokens that mimic the value of the original bitcoin.
- Stablecoins. These are one of the first and most popular categories of wrapped tokens. They are pegged at a 1:1 ratio to fiat currencies such as the dollar, so their value is always one dollar. When we talk about wrapped tokens, we must remember that they are based on two different blockchains. In our wrapped bitcoin (wBTC) example, it functions on Ethereum, but BTC operates on the Bitcoin network.
- wETH. Although ETH is Ethereum’s blockchain currency, it is incompatible with Ethereum ERC-20 tokens. Therefore you cannot directly exchange ETH for ERC-20 tokens without using a trusted third party such as a centralized exchange or other bridge.
To solve this problem, a group of Ethereum projects led by 0x Labs created an ERC-20 compatible token called wrapped Ethereum (wETH). To make wETH, you send ETH to a smart contract to lock it. The smart contract returns the wETH tokens to you at a 1:1 ratio. You can send wETH back to the smart contract to redeem the locked ETH. Various platforms facilitate this process, including Relay and Airswap.
It’s important not to confuse the two entities here: ETH is required to pay for transactions on the Ethereum network, while ERC-20 is the technical standard for issuing tokens on the Ethereum network. For example, Basic Attention Token (BAT) and OmiseGO (OMG) are ERC-20 tokens.
- renDOGE is a wrapped version of Dogecoin that can be mined using RenBridge via the RenVM protocol.
What is the future of wrapped tokens?
Achieving interoperability between different blockchains is a challenge for the crypto industry. One of the challenges is that as more and more blockchains become available, the number of bridges needed to enable cross-translation increases exponentially.
New solutions are being developed to make connecting assets across blockchains more accessible and efficient. One universal way to do this is to use a bridge hub to which all other blockchains connect.
Darwinia, a cross-chain bridge hub built on Substrate, is an example of this. Another well-known example project is Harmony’s Horizon Bridge.
There are other approaches to solving this problem. Major exchanges have recently launched their versions of wrapped tokens, for example, to offer compatibility between Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain. Not only does this now provide more flexibility in DeFi, but it is also a much cheaper alternative to Ethereum-based token transactions.
Many blockchains and cryptocurrencies have followed this lead, including the privacy-oriented cryptocurrency ZCash.
However, wrapped tokens are only in their infancy. In the future, we will see further development of these approaches, especially in creating decentralized methods of obtaining wrapped tokens instead of the centralized ones that exist today.






