Contents
Everyone interested in cryptocurrencies has heard about forks, but not everyone understands what they are. A fork occurs when blockchain participants need to agree on new uniform rules for the network (or, as they say, a consensus). In this case, the blockchain is split into two branches and participants must decide which branch they prefer.
The way things work is similar to society or family: the desire to revise an established social contract or balance of relationships often leads either to an agreed-upon renewal of this common contract or to conflict, which often results in divorce. In this case, there is a breakup into independent and incompatible families/states.
In the blockchain world, it is the same — some updates of the network are easy and coordinated (soft fork), while others, due to significant disagreements, lead to the division of the network into two independent parts (hard fork). This results in two blockchains and two independent cryptocurrencies.
Below we will explain in more detail how and why this is done. And most importantly, we will explain the most interesting part — how you can make money on it.
The brand new newsletter with insights, market analysis and daily opportunities.
Let’s grow together!
What kinds of forks are there?
Blockchain is a chain of blocks in which encrypted information about transactions made in the system is stored. It is an ongoing process, facilitated by network participants. Blockchains are based on open source software code that can be updated, trimmed or simply copied. Tampering with the source code and launching your own, modified network based on it is called a fork.
In the case of a fork one of two things happens: the division of the mother chain into two daughter chains, or the separation of a new chain from it (while preserving the old one). The chains begin to operate without being bound to each other and the characteristics of the coins change, even if no new cryptocurrency emerges. In other words, there is a successful consensus change in which the block is still recognized as valid.
There are two possible forks: soft fork and hard fork. The first is a soft fork where the old and new blocks remain relevant and a child is separated from the parent chain. Hard fork is a rigid modification of the program code, all old blocks are “forgotten,” and the blockchain now moves in two parallel lines.
Soft fork optimizes some characteristics of the coin, makes light cosmetic improvements. If some of the nodes do not accept such changes, they are still members of the network. This can be compared to the existence of an academic language and a dialect. Some people have chosen the dialect and communicate in it. However, the speakers of the academic language also understand them. The consensus remains.
The hard fork activation is a more radical technical solution, which is carried out without regard to compatibility with older versions. In this case, developers actually bury the old network. Users have to choose between two child chains, they become incompatible with each other, two different projects.
When a cryptocurrency is hardforked, one of the new chains can also die or be preserved. The consequences depend on the amount of hash rate power for each branch. The branch with the higher power has the highest chance of successful development and survival.
When is a soft fork needed?
Among the clear benefits of soft forks, experts cite the improvement of the functional qualities of a particular blockchain network. In addition, soft forks eliminate flaws and errors in the payment system. After a soft fork, the new algorithms continue to interact with the old rules, giving the network compatibility and users the right to choose whether or not to switch to the new software.
Improvements in one system force the other cryptocurrency team to upgrade as well. In other words, soft forks are normal, such cycles of updates and improvements stimulate competition in the market.
Another benefit of such soft updates is that systematic improvements to cryptocurrency networks allow them to expand their scope. For example, thanks to soft forks, one or another platform can be optimized for the banking sector. Implemented changes can be easily undone if they don’t take root or cause problems in the system’s operation.
There are few disadvantages to soft forks, it is the gentlest upgrade option. However, in some complex cases we need more radical solutions, for which soft fork is no longer suitable, and in these cases, hard fork is usually used.
When is a hard fork needed?
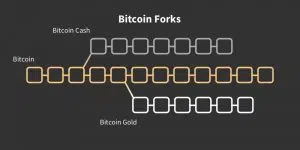
A hard fork involves introducing major changes to the blockchain, they split the chain into two separate chains, unable to interact with each other. This is how Bitcoin Cash, Bitcoin Gold, Ethereum Classic appeared, for example.
A striking example of a hard fork is the Ethereum fork, when the cryptocurrency was divided into two coins — the main Ethereum and additional Ethereum Classic (this is the old original version of the system). Many investors made good money on this.
Since almost all cryptocurrencies are open-source, theoretically anyone can make a hard fork. Usually, the initiators are active community members — developers, miners, famous leaders. After that, a group of like-minded people gathers and implements a plan for a hard fork.
Sometimes a hard fork can take place against the background of serious disagreements among community members. For example, this happened with the cryptocurrency Bitcoin Cash, which in November 2018 “split” into two branches (BCHABC and BCHSV).
![Wc8r_HrVO7sDWWiGQwxbED_83FGDVcFMgOTC8MAiZ6E[1] - buidlbee](https://buidlbee.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/Wc8r_HrVO7sDWWiGQwxbED_83FGDVcFMgOTC8MAiZ6E1-300x168.png.webp)
For members of the cryptocurrency community the hard fork of any major digital coin brings a number of multidirectional changes.
On the one hand, it is a personal benefit for each token holder. The value of the original currency is usually unchanged after the fork, and the new token is issued to anyone who has the original assets. While the first Bitcoin fork gave users a similar number of BCH coins, the next ABC hard fork with a face value of $100 coins also gave users ABC Cash in equal amounts with a value of $50.
Another benefit of a hard fork is that usually it gives an increase in the capitalization of the forked asset. It’s as if a new coin with good prospects enters the market, and investors who previously purchased the original token have every chance to make good money on it. Knowing this natural growth anyone can try to make money on it even after the hard fork.
However, don’t take hard forks too lightly — performing a large-scale or radical upgrade of an already working in production network is always a risk. It is dangerous to catch some unintended error and break an already working project. The consequences of such mistakes can often cost a project its life.
Any hard fork is a last resort when no other options are possible.
Why do forks take place?
Basically, there are two reasons: technical and ideological.
As official reasons, most often developers point to the need to improve technology and optimize the network. This is a kind of network upgrade, improvement of performance and correction of accumulated bugs.
As a rule, developers try to change the following:
- Increasing the size of the block. This is to make the block process more transactions per second.
- Reducing the commission. This increases interest in the coin from the cryptocurrency community.
- Increased bandwidth. This also increases the coin’s popularity in the cryptocurrency market.
The second frequent reason is ideological — often behind the fork are intranet squabbles among project leaders. Sometimes it can be a desire to centralize management or just an opportunity to make money. Often as a reason for the fork is called “loss of the true vision” of the project.
As a rule, such movements are not a good sign of cryptocurrency stability, though formally it is always declared to the contrary.
How to earn on hard forks?
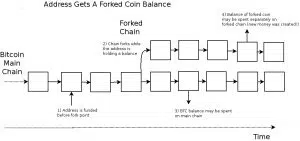
Users of exchanges that support hard forks, as a rule, get to their purse additional amount of new coins in the ratio of 1 to 1. Users do not need to do something for that, it happens by the fact of fork.
This is why a hard fork, for example, is preceded by a rapid rise in the rate. Users transfer their assets into cryptocurrency on the eve of the split, this doubles the number of coins after the fork. Placing coins on the exchange before the hard fork is the easiest and least expensive way to double the number of tokens (initial amount).
Another way is to track altcoins that disproportionately lose in value before the hard fork. This indicates that participants are temporarily transferring them into a cryptocurrency that is facing a hard fork. After buying altcoins in such a situation, the calculation is to return to the equilibrium exchange rate or even increase in the future when the hard fork occurs and the reversal begins. So you indirectly use the hard fork to enrich yourself even on assets that have nothing to do with it.
Experienced traders will enjoy making a short of such a coin, profiting from the depreciation of the asset in the short term. You can make a short either against an altcoin that loses in value due to temporary resource spillover (as described above), or against a weaker coin formed as a result of a hard fork.
For example, when BTC and BCH were forked, it was obvious for many that BCH was a weaker project by hash rate and prospects, so most sold BCH immediately after receiving them. The behavior of the price in that situation was easily predictable, so many opened a short position against BCH even without participating in the fork itself.
Keep in mind that a good short will require credit. Short positions are opened with the expectation to increase the deposit on decrease of the quotes. The exchanger opens a short sale on the descending trajectory (while the value of the asset is high). Then, some time later, he redeems the asset at the lowered price established at that moment on the market. In this way, the trader makes money on the difference by playing the market down in the short term.
As you can see, there are many ways to make money from the upcoming hardfork, above we have listed three different and most accessible. With this knowledge you now not only understand what forks are in the cryptocurrency world, but you will also be able to monitor the approaching forks yourself to try to make money on them.







