Contents
- 1 What Is a Central Bank Digital Currency (CDBC)?
- 2 History of CBDCs
- 3 Common CBDC features
- 4 What Is the Difference Between Cryptocurrency and CBDC?
- 5 How does central bank digital currency (CBDC) work?
- 6 Types of CBDCs
- 7 Goals of Central Bank Digital Currencies
- 8 Issues CBDCs Address and Create
- 9 Risks of CBDCs
- 10 Pros and cons to CBDCs
Central bank digital currencies are digital tokens, similar to cryptocurrency, issued by a central bank. They are pegged to the value of that country’s fiat currency.
Many countries are developing CBDCs, and some have even implemented them. Because so many countries are researching ways to transition to digital currencies, it’s important to understand what they are and what they mean for society.
What Is a Central Bank Digital Currency (CDBC)?
In absolute basic terms, central bank digital currency (CBDC) refers to ‘the digital form of a currency issued by its central bank’. This simple summative definition points towards two rife elements of a CBDC;
The brand new newsletter with insights, market analysis and daily opportunities.
Let’s grow together!
- That it is a currency, which implies it can be used as a means of exchange, and
- That it is digital in nature, implying that it employs adept technologies.
This article takes you through all you need to know about CBDCs so that you feel enlightened the next time you come across news of one being launched.
History of CBDCs
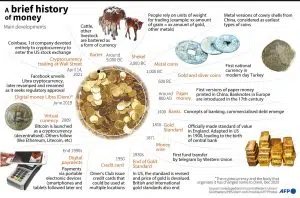
Because CBDCs are the latest forms of money, it is paramount to first understand how we got here. The picture below offers a nuanced 101 insight of how money has evolved from time immemorial.
The above picture does well but fails to tell us where and when this digital currency thing came from. That’s what we’re pivoting to right away.
Consider the economy as an old diesel-powered train, its fuel as currencies, its rail road as the technologies developing its fuel, and lastly central banks as the engineers who double up as the traffic marshalls on this railroad to open and close the gates to each station. Our train can only move as fast as the efficiency of our fuel and how well the engineers will allow it to run.
A noble person uttered sheer wisdom when they said ‘you cannot fight an idea whose time has come’. In the private sector, blockchain and other such technologies have been developed and adopted to birth cryptocurrencies that support settlements seamlessly. Central banks have been skeptically observing this adoption and some have finally come to terms with the fact that they must-needs do more to adopt such or similar technology.
Because of their skeptical nature, and of course the risks associated with cryptocurrencies, central banks are mulling launching their own digital currencies which they can fully back just like their fiat currencies. This is succinctly the position for most economies around the world – their trains are at their garage stations with engineers trying to figure out whether and how to adopt this new fuel technology they have heard and seen from cryptocurrencies.
It is upon this premise that CBDCs were and continue to be birthed. Let’s highlight some of the common features of this new development so that we understand it.
Common CBDC features
For starters, it is a child of central banks. This implies that it is issued and regulated by the monetary authorities issuing them, per se the central banks of their economies. From the brief history picture above, central banks abolished the gold standard in the 1930s thus essentially the currencies they issue since then are fiat currencies. (A fiat currency is a currency backed by the trust of its issuing authority, often the central bank. It is not backed by reserves.)
As such, the digital currencies central banks birth again are in tandem fiat currencies based on their earlier issued currencies. Being issued by central banks, they also enjoy a ‘legal tender’ status implying that parties are obliged to take them in settlement of financial transactions.
Such currencies ride on distributed ledger technologies for settlement of transactions such that they can initiate and terminate debit and credit entries on the ledgers. These features can be summarily presented as follows;
Key Takeaways from the most common features of CBDCs
- They are issued and regulated by central banks
- They are fiat currencies
- They are legal tender.
- They employ distributed ledger technologies
What Is the Difference Between Cryptocurrency and CBDC?
Already some glaring differences are noticeable between the features of cryptocurrencies and CBDCs. Here are the key ones at a glance.
| Cryptocurrencies | Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) |
|
|
How does central bank digital currency (CBDC) work?
We noted earlier that CBDCs are based entirely on the fiat currencies of the issuing central banks. Essentially, CBDCs work the very same way as fiat currencies; but of course with the digital convenience.
Consider this, you were shopping around for a car and came across a slightly used 2021 Tesla Model 3, which happens to be your most coveted electric car. The dealer is asking US $50,000 for it on a first-come-first-served basis; implying whoever offers the US $50,000 first drives home with it. Of course the dealer doesn’t want to handle physical cash for all the valid reasons, so they demand the amount either be deposited to their accounts or you swipe your card. Unfortunately this amount is above your daily card limit so your bank cannot authorize the transaction even though you have way more than that in your account.
You’re left with just one option if you really want to bag the deal – rush to your bank to make the deposit. So you walk to the next block into your banking hall and authorize the transaction to your dealer’s account and bring him the bank’s receipt note. If they bank with a different bank, that amount may not even hit their accounts anytime from when you make the deposit to a few hours or even days. This is the time it takes for the banks to settle the transaction on you and your dealer’s behalf.
Now consider a situation where your country’s central bank operates a CBDC. With the advent of technology, you need not go to the bank for such and neither does your dealer need to wait for hours or days before the money hits their accounts. And oh yes, you won’t even be charged a fortune for this transaction by the banks!
You just log in to a platform provided by your central bank and after authenticating yourself you transfer the US $50,000 to your dealer instantly! Yes! And almost at zero transaction charges! Sounds like a dream? Well, some are already living it because that’s exactly how CBDCs work!
Types of CBDCs
Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) are of three major types; majorly just two types, and the third is a hybrid of the two.
- Wholesale CBDCs – these are CBDCs primarily used by financial institutions; predominantly those that hold deposits with central banks. They are mainly used for inter-bank transfer settlements.
- Retail CBDCs – these are CBDCs primarily used by consumers and businesses; much so like physical currencies in settling financial obligations.
- Hybrid CBDCs – these types of CBDCs have both retail and wholesale characteristics.
It is worth noting that retail CBDCs are further classified into two depending on how their users can access and use their currencies. They can be either account or token based. Account-based retail CBDCs require user accounts with a form of digital identification to operate, whereas token-based retail CBDCs require private/ public keys for operation.
The implication of retail CBDCs being either account-based or token-based is that the token-based ones offer anonymity in transactions as public/ private keys are required to authenticate and use the CBDCs; unlike account-based ones which require individuals to authenticate their account profiles with the central banks.
Goals of Central Bank Digital Currencies
Without beating around the bush, the main goal of CBDCs is to employ existing technology to provide convenience, accessibility, transferability, financial security and layered privacy to businesses and consumers in an economy. It is beyond common knowledge what more CBDCs can do, but it is appropriate to include the following among the goals of CBDCs:
- To provide an avenue of convenience in financial transactions by improving the access, transferability, financial security and privacy.
- To improve financial inclusion in an economy by serving those who may not be served by other financial institutions (banks).
- To provide central banks with another avenue by which monetary policy can be effected to bring about economic growth, curb inflation and provide stability in an economy.
- To reduce the infiltration and reliance on other forms of currencies such as cryptocurrencies which are prone to volatility in the economy.
Issues CBDCs Address and Create
Although it is not elaborately backed by sufficient data due to the short time they have been existent, CBDCs address and create some issues in the financial environment. Key among the issues fronted that they address include the following:
- Financial inclusion by expanding access to the general public
- Reducing the reliance on cryptocurrencies which are prone to volatility
- Reduction in the cost and time it takes to make settlements.
- Reduction in the reliance of banks to fulfill financial transactions
Although CBDCs address the aforementioned issues in a noble manner, they also bring about the following issues:
- Cybersecurity entailing privacy and protection when carrying out financial transactions
- Monetary policy influence by affecting the role of commercial banks in financial transactions
Risks of CBDCs
The major risks associated with CBDCs are a combination of risks associated with dealing in/ with fiat currencies as well as digital technologies. Seeing that they are issued by central banks their risks are quite minimal relating to fiat currencies, thus the major risks entail cybersecurity concerns when dealing with digital technologies.
Pros and cons to CBDCs
Summarily, the following are the key pros and cons relating to CBDCs
| Pros of CBDCs | Cons of CBDCs |
|
|



![Central-Bank-Digital-Currency-CBDC[1] - buidlbee](https://buidlbee.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Central-Bank-Digital-Currency-CBDC1-300x82.png.webp)
![-1x-1[1] - buidlbee](https://buidlbee.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/1x-11-300x164.png.webp)



