Contents
In our guide, we describe the distinctive features of all 7 major blockchains that position themselves as “Ethereum killers.” They all have basic Ethereum functionality, such as smart contracts and DApps, but have some advantageous features of their own, which we will discuss next.
Avalanche: optimized Ether
Avalanche was invented by Emin Gün Sirer, a Turkish-American computer scientist, professor at Cornell University, and founder of Ava Labs. Prior to Avalanche, Sirer worked on various operating systems as well as scaling and security solutions for Bitcoin.
While working on Avalanche, Sirer tried to solve the main problem of modern blockchains: slowness. Even the most advanced blockchains conduct transactions several dozen times slower than the systems owned by Visa and Mastercard. Avalanche, at its peak, is capable of processing 5,000 transactions per second, making it hundreds of times faster than Ethereum.
The brand new newsletter with insights, market analysis and daily opportunities.
Let’s grow together!
Avalanche achieved this impressive speed thanks to a fundamentally different consensus algorithm. While in the case of Ethereum, all nodes in the network must be fully synchronized, in Ava, one node communicates with a limited number of nodes that together form a network segment, or the so-called Gossip Network. This segmentation allows a significant increase in speed. In fact, it is a heavily modified PoS consensus that modern Ethereum uses.
Otherwise, Avalanche supports a fairly standard set of features: creating smart contracts, decentralized applications, and running its own private and public blockchains.
Most experts attribute the record rise of $AVAX’s altcoin price at the end of 2021 to $138 and a partnership agreement that the platform’s creators signed with Deloitte, one of the world’s largest consulting firms. Under the terms of the agreement, Avalanche and Deloitte will develop a solution that will improve the U.S. Federal Emergency Management Agency. $AVAX has been growing quite steadily for the last year, although it is far from reaching its previous peak.
The main differences from Ethereum are greater speed and an improved PoS consensus algorithm. It is the most technically similar (but improved) solution to the original Ethereum in today’s review.
Solana: the fastest blockchain ever
This project’s white paper describes Solana’s main goal: speeding up the blockchain (or, technically speaking, speeding up network consensus). The high speed should help developers scale their decentralized applications (dApps) and automatically provide them with fast user base growth, the whitepaper says.
To speed things up, Solana uses its own proprietary Proof of History (PoH) consensus algorithm together with the Proof of Stake (PoS) algorithm. With PoH, nodes in Solana’s blockchain can create blocks without having to “negotiate” their actions with the entire network. You can think of PoH as a cryptographic clock; it marks transactions with a hash, which guarantees that the transaction actually happened in time. This significantly speeds up transaction times.
If Solana proclaims speed as its main killer feature, let’s compare it and other cryptocurrencies in terms of transactions per second:
- Bitcoin (BTC) averages 6 transactions per second.
- Ethereum (ETH) has 25 transactions per second.
- Avalanche (AVAX). This platform can process about 5,000 transactions per second.
- Visa’s network can handle 24,000 transactions at a time.
- Solana (SOL) boasts an astronomical 60,000 transactions per second.
But Solana also has disadvantages — its high instability of operation makes it an unwilling price to pay for speeding up at any cost. As an example, here is just one of the most notorious cases:
- In June 2022, Solana did not work for four hours because of an error in the code, resulting in the cryptocurrency price dropping by 11% during the day. After the bug was fixed, the developers had to restart the blockchain. There have been dozens of such cases, which have given rise to sarcastic memes about Solana.
We must admit that Solana is working hard to improve the network, and a big upgrade in 2023 (Firedancer validators will be added) will most likely put an end to the numerous technical problems of this blockchain.
Firedancer is a next-generation independent validator client for the Solana blockchain that is intentionally designed for performance. In addition to performance improvements, the Firedancer client may make running Solana nodes cheaper as it is designed to be more efficient.
The main difference from Ethereum is that it works at the speed of light, which makes such a blockchain suitable for the distribution of media content, which is why Solana is now the second most popular among NFT creators. The downside of this acceleration is the instability of the blockchain and its centralization.
Polkadot: a blockchain aggregator
The Polkadot project’s main idea is to provide compatibility between different blockchains within one platform; Polkadot is like linking different blockchains into one common blockchain (a so-called “parachain”).
Polkadot forms a single space of synchronized blockchains. A parachain is the ability to work transparently on multiple blockchains at once, exchanging data and tokens freely between them as if they were a single network.
Polkadot was created by Gavin Wood, the second co-founder of Ethereum who left the project in 2016 due to disagreement with the future course of Ethereum. If each blockchain moves on its own separate path of development, Gavin decided that it was necessary, on the contrary, to create a kind of common environment that would unite this diversity into a single whole.
Thanks to the famous founder and the unique niche that the project has occupied, the following can be said about Polkadot:
- This project is one of the top 5 most generously funded blockchain projects in the world. It has received more than $230 million in investments.
- Polkadot is the most actively developing project. According to Santiment’s rating, in terms of the frequency of platform updates, it is currently in first place among all cryptocurrencies.
The main difference from Ethereum is that the project positions itself as a multi-linking blockchain (parachain), which will unite all other large networks, which in the long run will make it the unique and central crypto project of the world. Judging by the successful funding of the project, at least investors believed in this idea.
Cardano: a multi-layered blockchain
Cardano (ADA) is a blockchain platform created with the collaboration of Charles Hoskinson, former co-founder of BitShares, Ethereum and Ethereum Classic. From the beginning, it has been positioned as an advanced alternative to Ethereum.
Cardano cryptocurrency (ADA) uses its own blockchain called Cardano Settlement Layer (CSL). CSL is a distributed transaction registry layer to support cryptocurrency wallet transactions. The second layer, called the Cardano Computation Layer (CCL), will support smart contracts and decentralized applications.
In other words, if usual blockchains have the second layer as external projects (for example, for Ethereum, such an add-on is Polygon), then in Cardano everything is initially built as one multilayer project. Each individual layer (so far there are only two) solves its own specialized task. This layered architecture allows for the blockchain to be speed up and be made very versatile.
According to public statistics, Cardano is also very actively being developed, now it is in 3rd place by the frequency of project code updates.
The main difference from Ethereum is that Cardano is characterized by increased stability and security of operation, which are achieved by its multi-layer blockchain. As for speed, Cardano is much faster than Ethereum, providing 257 transactions per second, but it is strongly behind both Solana and Avalanche.
Cosmos: blockchain hosting
The Cosmos ecosystem is positioned as an internet of blockchains. Blockchains launched on the Cosmos Network can communicate with each other through the underlying Cosmos Hub blockchain via the inter-blockchain communication protocol.
Cosmos Hub is a cross-chain solution that allows any blockchains to be launched based on the Cosmos ecosystem to communicate with each other as well as with external networks such as Ethereum and Bitcoin.
Simply put, Cosmos is a new kind of blockchain builder that allows you to design and run your own specialized blockchain-based solutions on the basis of its ecosystem for all occasions. The project calls this concept a “blockchain internet” or “blockchain 3.0.”
The main difference from Ethereum is that while only new tokens and applications can be launched on Ethereum, Cosmos ($ATOM) has gone even further, allowing custom blockchains with their own functionality to be launched in their environment while linking them at will to internal and external blockchains. Cosmos has also raised a gigantic amount of investment — $500 million — which allows him to feel confident in the market.
Aptos: Solana’s killer
Aptos ($APT) is the newest blockchain discussed in this list and was launched in summer 2022, in the midst of crypto winter. Aptos was promoted under the “Solana killer” slogan. Large investors (Binance Labs, FTX Ventures, Coinbase, and a16z, among others) invested in blockchain for about $350 million, and the project entered the Top 20 cryptocurrencies by market capitalization, which made its launch very loud.
To understand the specifics of Aptos, it is important to know its backstory. Aptos was originally created by former employees of a division that was part of Meta. This division for more than four years was engaged in the creation of Web 3.0 services for Facebook and the development of a corporate blockchain Libre, which was subsequently renamed to Diem. However, this innovative blockchain from Facebook, under the strongest pressure from regulators, was eventually shut down.
After the project was shut down, the developers quit their jobs and decided to open their own independent startup based on the technology they had already developed. Knowing the star team that stands behind Aptos, the startup was supported by the largest investment funds.
Aptos is a blockchain that declares its focus on scalability and security. The developers are using a new programming language, Move, which tries to solve all the problems of Ethereum’s Solidity language.
But the most important thing the developers claim is that they know how to achieve an incredibly fast processing speed of 130,000 transactions per second. The current network is much slower, but the developers have guaranteed that this speed will be achieved in the future after upgrading the standard PoS consensus. Usually, the consensus protocol agrees on transactions, order of execution, and result, but in Aptos, it will be separated from transaction execution completely.
I think @sandeepnailwal is definitely wrong
I agree with Aptos, Avalanche and Cardano but Solana has already established network effects and branding
As in the discussion is over. Let’s also not forget the best UX by far pic.twitter.com/wPXyVtoiVY
— 585.ETH (@585Eth) February 24, 2023
It is worth noting that the GitHub page for the project is now one of the most popular in the category of blockchain development on GitHub. The project has started a grant system to attract investments of funds, and third-party developers now have the possibility to earn very good money on Aptos.
On the one hand, the presence of large investment funds is an acknowledgement of the project on the part of business. On the other hand, it is very alarming. Considering that almost half of all blockchain token issuance belongs to corporations, there is a risk of their price manipulation and even control over blockchain.
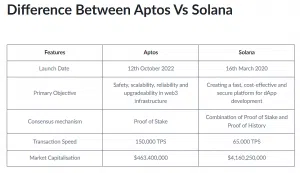
And since Aptos compares itself everywhere with Solana, let’s give them a general comparison in a table:
The main difference from Ethereum is that the most important problem of Aptos is that this blockchain is still young and needs to be finalized; all the declared parameters are yet to be proven in the coming years. On its own, Ethereum is definitely an established project with its own audience.
Tezos: democracy on the blockchain
Tezos (XTZ) burst onto the crypto scene in July 2017 with a phenomenally successful ICO, raising $232 million. It was a record at the time, but that amount has now turned into $600 million due to rising crypto prices. However, this success was followed by scandalous disagreements between the project founders, who could not divide the authority and the resources raised. All of this led to lengthy lawsuits and delays in the release of the token.
The cult magazine Wired at the time wrote about Tezos as “a reminder for us all that the greed of the few could ruin great ideas and ventures for everyone.” It wasn’t until three years later, in 2020, that the leadership of the Tezos Foundation changed and the project, which had already gained a scandalous reputation, finally began developing the blockchain itself.
Tezos is a platform for hosting smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). Its native cryptocurrency is called Tez, or Tezzie (XTZ). The differences from Ethereum start at the consensus level.
Tezos uses liquid proof-of-sctake (LPoS) as consensus. Users can send Tezos tokens (XTZ) into the stack, receiving rewards for doing so and having the ability to make decisions about changes within the blockchain. “Liquid” means that coins can be easily withdrawn from stacking at any time without a blocking period like Ethereum, which is very useful.
There are also additional important differences from Ethereum’s standard approach:
- The Tezos blockchain is inherently extremely flexible to make changes — any edits and updates to the blockchain code do not require a fork like all other blockchains. The governance here is DAO-style, which simplifies the upgrade and development of the blockchain, which is decided by online voting among token holders.
- Highly secure and functional smart contracts are implemented here. The particular reliability and security of Tezos smart contracts are achieved by using a specific Michelson programming language written specifically for Tezos smart contracts.
1/ Big Names Interacting With Tezos
Manchester United
New York Mets
McLaren
Red Bull
Ubisoft
GAP
Evian
Papa John’s
Cleveland Cavaliers
Cambridge University$XTZ— The Half Soul (@The_Half_Soul) June 7, 2022
The main difference from Ethereum is that despite its reputation being ruined by the long legal disputes between the founders of the project, Tezos is trying to implement a democratic model of project self-management at the blockchain level (through an open vote of its token holders). This is a very bold approach against the background of the closed and conservative Ethereum governance, where all strategic decisions are made by a limited group of people.



![Seven[1] - buidlbee](https://buidlbee.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Seven1-300x271.jpg.webp)